Generative AI is revolutionizing how businesses operate, enabling faster innovation, personalized customer interactions, and creative problem-solving at an unimaginable scale. But as this technology becomes more integrated into everyday operations, organizations face an urgent question: how do you reap the rewards of GenAI without exposing your business to its inherent risks? From data breaches to sophisticated phishing attacks, the threats linked to GenAI are as dynamic and advanced as the technology itself. The stakes are high, and the need for robust risk management strategies has never been more critical.
This blog explores the transformative potential of Generative AI, the challenges it introduces, and the solutions that can address them. Whether you’re grappling with compliance complexities, mitigating the fallout of data leaks, or seeking proactive ways to guard against malicious AI misuse, understanding the landscape is the first step. Discover how forward-thinking strategies and cutting-edge tools can help your organization embrace GenAI confidently and securely.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI, or GenAI, represents a groundbreaking leap in artificial intelligence technology, enabling machines to create content that closely mimics human output.
Unlike traditional AI, which analyzes data to identify patterns or predict outcomes, GenAI produces entirely new content—text, images, audio, or video. This capability is driven by advanced models trained on vast datasets, allowing them to generate everything from realistic dialogue and visually stunning artwork to sophisticated code snippets. Its applications are vast and varied:
- Marketing teams rely on GenAI to craft personalized campaigns.
- Developers use it to accelerate software prototyping.
- Customer service departments integrate AI-driven chatbots to handle inquiries with human-like fluency.
These capabilities are not just tools but catalysts for innovation across industries.
With such transformative potential comes an equally significant set of responsibilities. GenAI’s ability to mimic human behavior so convincingly introduces unique security challenges. For instance, its capacity to generate realistic text opens the door to hyper-personalized phishing scams, while its reliance on vast datasets raises concerns about privacy and data leakage.
As businesses increasingly adopt these technologies, understanding their benefits and risks becomes essential for harnessing their full potential while safeguarding organizational integrity.
What are the Risks Associated with GenAI?
While Generative AI offers transformative benefits, its adoption introduces significant risks that organizations must address to ensure safe and effective use.
One of the most pressing concerns is data leakage—a risk amplified by the extensive datasets required to train and operate GenAI systems. Sensitive information can inadvertently be retained and exposed during interactions, jeopardizing privacy and compliance with data protection regulations.
Another critical threat is the malicious use of GenAI. Cybercriminals can exploit their capabilities to craft realistic phishing emails, generate harmful content, or automate sophisticated scams, increasing the scale and effectiveness of their attacks.
Compliance failures also arise as organizations navigate the complex legal landscape surrounding AI usage. Missteps in governance or lack of transparency can lead to regulatory violations, hefty fines, and erosion of stakeholder trust.
The consequences of these risks extend beyond immediate operational disruptions. For instance, a single data breach can expose confidential customer information, damaging an organization’s reputation and leading to financial losses. Similarly, falling victim to malicious use of AI tools can compromise intellectual property, weaken internal defenses, or even disrupt critical business functions. Compliance failures, on the other hand, can result in regulatory audits, legal battles, and the loss of customers wary of weak governance practices.
By understanding the broader implications of these risks, organizations can better appreciate the necessity of implementing safeguards and proactively addressing vulnerabilities. This foundation sets the stage for exploring real-world examples demonstrating how these risks can manifest in practice.
Example 1 – Data Leakage
A financial services firm integrates a generative AI chatbot to assist with customer inquiries about account balances and transaction histories. During training, the chatbot inadvertently absorbs sensitive client data from its development environment, including account numbers and transaction details. Later, a customer inquires about general financial advice, and the AI erroneously generates a response that contains snippets of another customer’s account details.
The exposure is traced back to insufficient data sanitization before training the model. This mistake erodes customer trust and results in a major data breach under GDPR regulations, leading to hefty fines and a tarnished reputation.
Example 2 – Malicious Use
A cybercriminal group uses a generative AI tool to craft hyper-realistic phishing emails. For instance, the attackers create an email seemingly sent by the HR department of a healthcare organization, announcing updates to employee benefits.
The email includes:
- A forged sender name mimics the HR manager.
- Perfect grammar and tone consistent with the company’s communications.
- A link to a fraudulent login page replicating the company’s benefits portal.
Employees unsuspectingly enter their credentials, granting attackers access to sensitive internal systems. Within days, patient records and proprietary research data are exfiltrated and later sold on the dark web, illustrating how GenAI enhances the precision and believability of social engineering attacks.
Example 3 – Compliance Risks
An e-commerce company employs a generative AI system to analyze customer reviews and suggest improvements to product descriptions. However, during its analysis, the AI unintentionally gathers and stores personally identifiable information (PII) from unmoderated reviews, including customer email addresses and order details.
A compliance audit flagged the company’s lack of clear governance policies on data usage and retention for AI systems. Regulators discovered that the company violated CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) rules by failing to protect customer PII and not providing an opt-out mechanism for AI data processing.
The result? The company faces a $5 million fine, mandatory audits for the next three years, and negative media coverage that drives away privacy-conscious customers.
How Can Organizations Protect Themselves from GenAI Risks?
Protecting against the risks associated with Generative AI begins with implementing a comprehensive framework for AI risk management. This framework should establish clear policies that define how AI tools can be used, the data they can access, and the safeguards required to ensure security and compliance. Regular audits and monitoring of GenAI deployments are critical in identifying vulnerabilities, such as improper data handling or weak access controls before they can be exploited. Equally important is empowering employees with the knowledge to recognize and mitigate AI-related risks. By providing targeted training, organizations can ensure their teams are equipped to use AI responsibly while remaining vigilant against potential threats.
In addition to foundational policies and training, leveraging advanced security solutions is essential to building a resilient defense. Tools that offer comprehensive visibility into AI usage enable organizations to monitor where and how GenAI applications are deployed, ensuring no unauthorized tools operate unnoticed. Automated policy enforcement further strengthens security by reducing reliance on manual processes, ensuring compliance is maintained consistently and efficiently. Just-in-time security guidance adds another layer of protection by delivering real-time insights to users, helping them make informed decisions while interacting with AI systems.
AI Risk Management – What is the Probability of Getting Harmed by GenAI?
AI Risk Management is the cornerstone of safeguarding organizations against the potential harm of Generative AI. This discipline involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with AI systems to ensure they operate securely and responsibly. The probability of harm from GenAI depends on several factors, including the sensitivity of the data it accesses, the organization’s level of preparedness, and the robustness of its governance policies. For instance, an AI tool handling highly sensitive customer information presents a higher risk profile than one for generic content generation.
Proactive risk management strategies reduce the likelihood and impact of harm. Automating governance processes, such as real-time monitoring and policy enforcement, ensures that vulnerabilities are detected and addressed before they escalate. Equally important is the availability of actionable insights—tools that provide clear, timely recommendations that empower teams to respond to risks effectively and without delay.
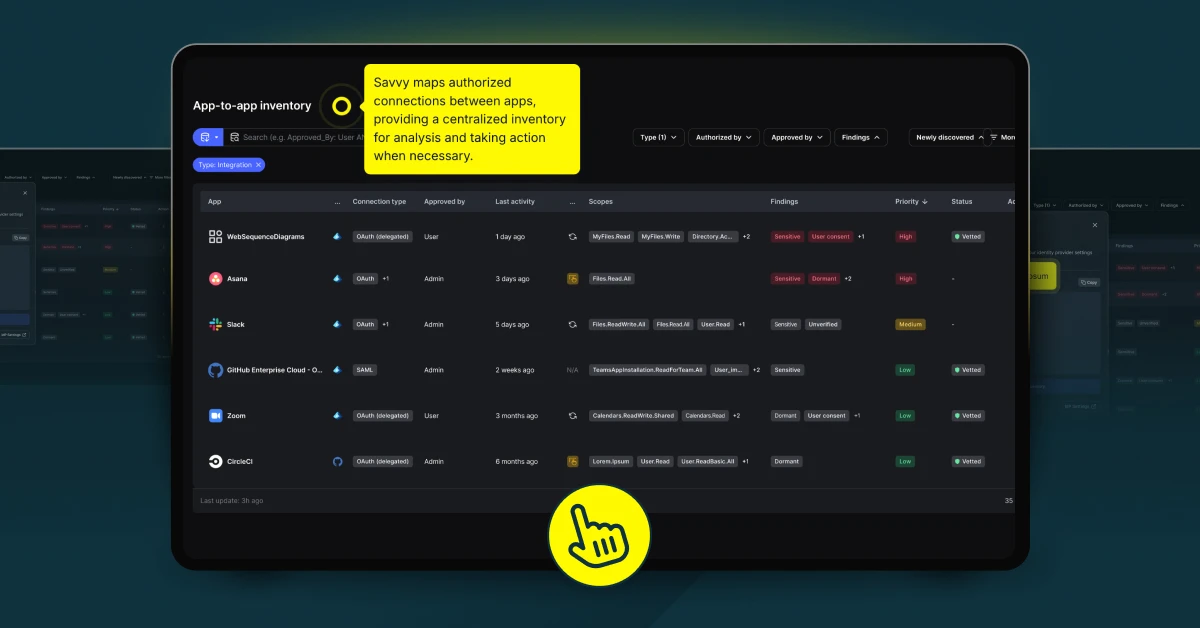
Savvy Manages GenAI Risks
Managing the risks associated with Generative AI requires more than policies and training—it demands enterprise-grade solutions that seamlessly integrate into an organization’s existing security ecosystem.
Savvy’s approach to GenAI risk management empowers businesses with the tools they need to stay secure while embracing innovation. By providing comprehensive visibility into GenAI applications, Savvy ensures that organizations can monitor AI usage across their environments, identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities before they become threats. Automated policy enforcement further strengthens governance, ensuring compliance is maintained effortlessly and consistently.
Savvy doesn’t stop at visibility and automation—it enhances organizational resilience with just-in-time security guidance. This feature delivers real-time recommendations tailored to specific interactions, enabling users to navigate AI systems safely without disrupting their workflows. Whether managing data leakage risks or ensuring adherence to complex regulatory frameworks, Savvy equips organizations to take proactive, informed steps toward safeguarding their operations.
Ready to protect your business from GenAI risks? Get a Demo today!
FAQs
Is GenAI Secure?
- Generative AI can be secure when properly managed, but it inherently carries risks like data leakage and misuse if safeguards are not in place.
What is GenAI in cyber security?
- In cybersecurity, Generative AI refers to AI systems that can create content, posing both opportunities for innovation and risks such as enabling more sophisticated cyberattacks.
What are the disadvantages of GenAI?
- Disadvantages include potential data leakage, malicious misuse for phishing or misinformation, and challenges in maintaining compliance with privacy regulations.